Introduction
In today’s increasingly digital world, cybersecurity has never been more critical. As businesses and individuals depend more on the internet for daily operations and activities, the risks of cyberattacks, data breaches, and online fraud continue to rise. Cybersecurity is essential to protect sensitive information, maintain privacy, and ensure the secure functioning of systems across various industries. This article will explore what cybersecurity entails, its importance, the most common threats, and how individuals and businesses can enhance their digital security.
What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practices, technologies, and processes designed to protect computer systems, networks, and data from cyberattacks. It encompasses a range of defensive mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access, theft, damage, and disruption to digital systems. Cybersecurity is critical across all sectors, from banking and healthcare to government and education.
Effective cybersecurity relies on multiple layers of protection, including software, hardware, human factors, and organizational policies.
Why is Cybersecurity Important?
With the rise of digital technologies, cybersecurity has become essential for ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data. Some reasons why cybersecurity is critical include:
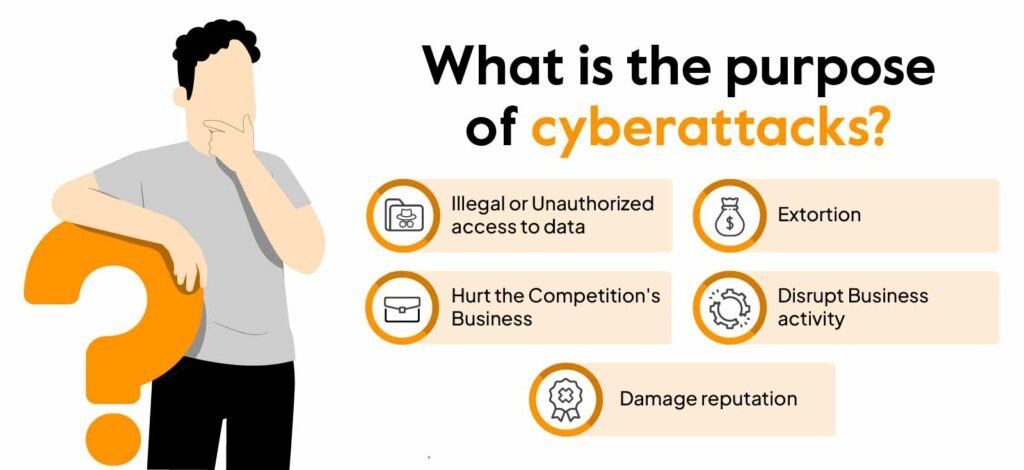
- Protection of Sensitive Data: Businesses and individuals store large amounts of personal, financial, and confidential information online. Without cybersecurity measures, this data is vulnerable to theft and misuse.
- Prevention of Financial Loss: Cyberattacks can lead to significant financial losses, both from the theft of funds and the costs of recovering compromised systems.
- Safeguarding Reputations: A data breach can damage the reputation of an organization, leading to lost business and consumer trust.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations that mandate certain cybersecurity measures. Non-compliance can result in legal penalties and fines.
- Maintaining System Integrity: Cybersecurity ensures that computer systems continue to operate efficiently and without disruption. Cyberattacks such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) can bring down entire systems, causing operational paralysis.
Common Types of Cybersecurity Threats
Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics, making it essential to understand the various types of cyber threats. Here are some of the most prevalent cybersecurity risks:
1. Malware
Malware is malicious software designed to harm or exploit a computer system. It includes viruses, worms, ransomware, and spyware. Malware can infiltrate systems through infected emails, malicious websites, or software downloads.
2. Phishing Attacks
Phishing involves sending fraudulent emails or messages that appear to come from a legitimate source, tricking recipients into revealing personal information, such as passwords or credit card details. Phishing is one of the most common forms of cyberattacks due to its simplicity and effectiveness.
3. Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts the victim’s data and demands a ransom for its release. In many cases, even if the ransom is paid, the data may remain encrypted or corrupted.
4. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks flood a server with an overwhelming amount of traffic, rendering it unable to function properly. These attacks can bring down websites, disrupt services, and cause significant financial losses for businesses.
5. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
In a MitM attack, a cybercriminal intercepts communication between two parties to steal data or inject malicious content. These attacks typically occur over unsecured networks, such as public Wi-Fi, making users vulnerable to interception.
6. Insider Threats
Not all cyber threats come from external attackers. Insider threats occur when individuals within an organization—such as employees or contractors—intentionally or unintentionally compromise the security of the system. This may involve stealing data, installing malware, or sharing sensitive information.
How to Strengthen Cybersecurity: Best Practices for Individuals
Every individual plays a role in ensuring a safer digital environment. By adopting the following cybersecurity best practices, people can better protect themselves from cyberattacks:
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
Passwords are often the first line of defense in securing online accounts. Using strong, complex passwords—ideally 12-16 characters long and combining letters, numbers, and special characters—makes it more difficult for cybercriminals to crack them. Additionally, avoid using the same password across multiple accounts.
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring more than just a password to log in to an account. Typically, this involves entering a code sent to a phone or email or using a fingerprint or face scan.
3. Update Software Regularly
Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software to gain unauthorized access to systems. Regularly updating operating systems, applications, and antivirus software ensures that security patches are applied to prevent potential breaches.
4. Beware of Phishing Scams
Phishing attacks are designed to trick users into providing sensitive information. Individuals should be cautious of unsolicited emails or messages that ask for personal information, especially if the communication contains suspicious links or attachments.
5. Use a VPN for Secure Internet Browsing
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts internet traffic, ensuring that sensitive information is protected when browsing, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
6. Backup Important Data
Regularly backing up important files to an external drive or cloud storage ensures that data is recoverable in case of a cyberattack, such as ransomware.
Strengthening Cybersecurity for Businesses
Businesses, regardless of their size, are frequent targets of cyberattacks. Implementing robust cybersecurity practices is essential to safeguard corporate data, customer information, and the organization’s reputation.
1. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Businesses should regularly assess their cybersecurity risks to identify vulnerabilities in their systems. This can help in understanding which areas need more robust protection and inform security policies.
2. Employee Training and Awareness
Human error is one of the most significant causes of cybersecurity breaches. Providing cybersecurity training to employees can reduce the likelihood of phishing attacks, weak passwords, and other common security failures.
3. Implement Endpoint Security Solutions
Endpoint security ensures that all devices connected to a corporate network, such as laptops, mobile devices, and workstations, are protected. Installing antivirus software, firewalls, and monitoring tools can prevent malware from infiltrating systems.
4. Utilize Encryption for Sensitive Data
Encryption converts data into unreadable code, which can only be decrypted by those who have the correct encryption key. Businesses should encrypt sensitive data, such as financial records or customer information, to prevent unauthorized access.
5. Monitor and Respond to Cyber Threats
Businesses should invest in cybersecurity tools that monitor for suspicious activity and alert IT teams to potential breaches. Additionally, having an incident response plan in place ensures that the company can react quickly in the event of an attack, minimizing damage.
6. Ensure Regulatory Compliance
Many industries have specific regulations governing data security and privacy, such as GDPR in Europe or HIPAA in the healthcare sector. Adhering to these regulations not only protects the business from legal consequences but also builds trust with customers.
The Future of Cybersecurity: Emerging Trends
As technology evolves, so too will the tactics and tools used by cybercriminals. Here are some emerging trends in cybersecurity to watch for:

1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
AI and machine learning are being integrated into cybersecurity systems to identify and respond to threats in real time. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to detect unusual activity, automate responses to low-level threats, and predict potential vulnerabilities.
2. Zero Trust Security
The zero-trust model assumes that every user or device attempting to access a system is a potential threat. Instead of assuming that users inside the network can be trusted, zero-trust security continuously verifies the identity of all users and devices.
3. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize encryption. While it could enhance cybersecurity by developing more advanced encryption methods, it could also make current encryption systems obsolete, creating new challenges in securing data.
Conclusion
In an era where our lives are increasingly connected to the digital world, cybersecurity is no longer optional but a necessity. From individuals managing personal data to businesses safeguarding sensitive customer information, taking proactive measures to protect against cyber threats is essential. Understanding the common types of cyberattacks and adopting best practices for prevention can significantly reduce the risk of becoming a victim.
As cyber threats continue to evolve, so must our approaches to security. By staying informed, vigilant, and adaptable, we can safeguard our digital futures and build a more secure online environment for everyone.